- Home
- About
- Research
- Banana variety research
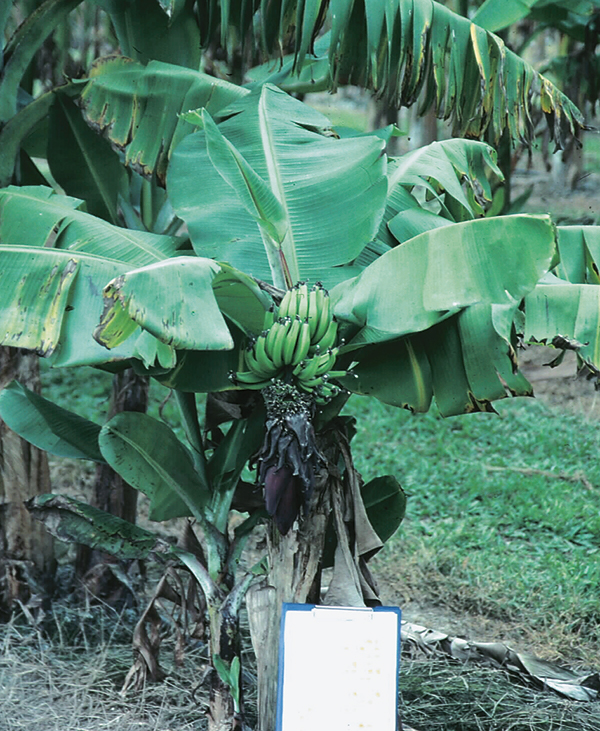
- Agronomic evaluation of new varieties South Johnstone screening trials (December 2022)
- Agronomic evaluation of new varieties – South Johnstone screening trial (October 2020)
- Agronomic evaluation of new varieties – South Johnstone (2018)
- Developing new resistant varieties Goldfinger mutagenesis trial
- Panama TR4 variety screening trial – Northern Territory (2018)
- Panama R1 variety screening trial (New South Wales)
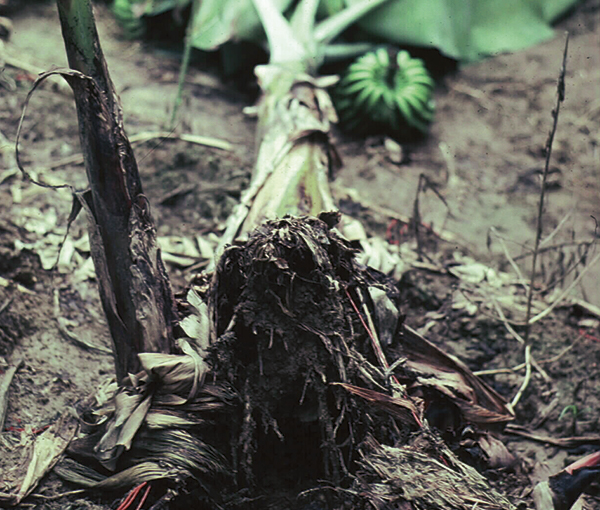
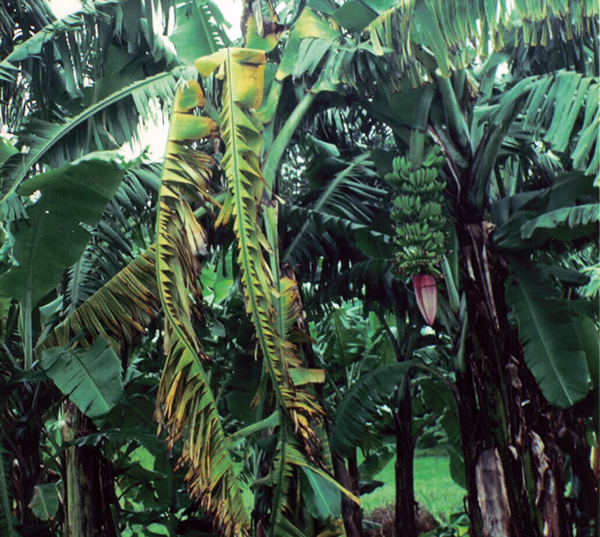
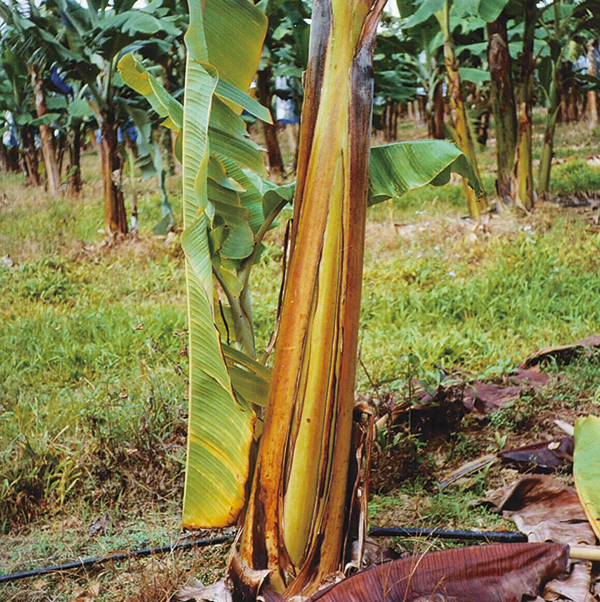
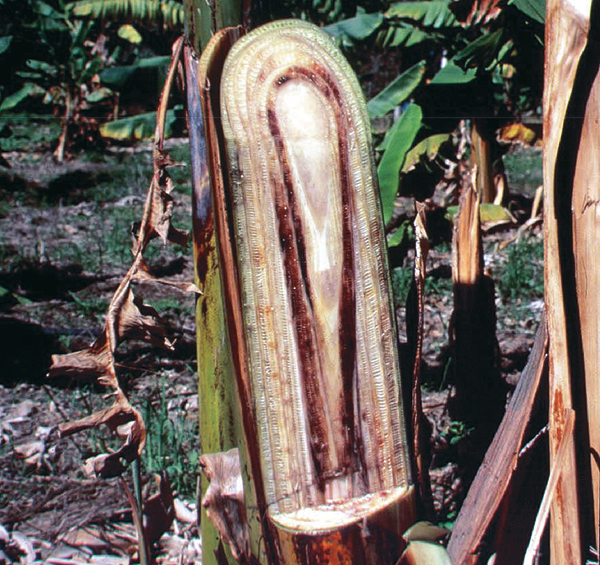
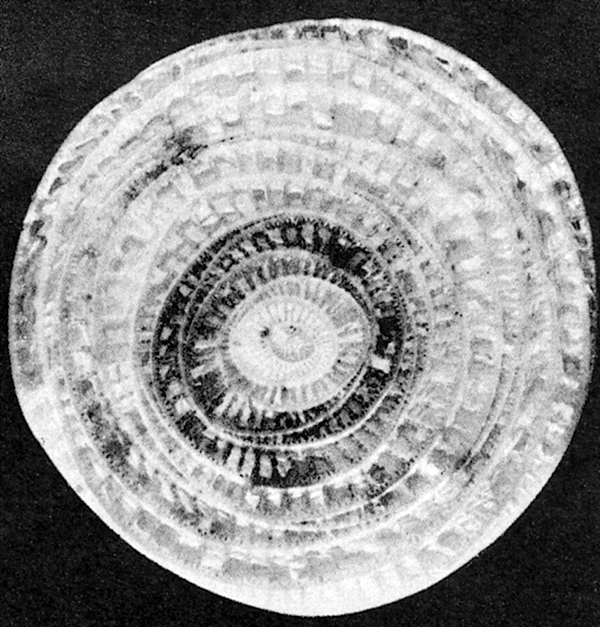
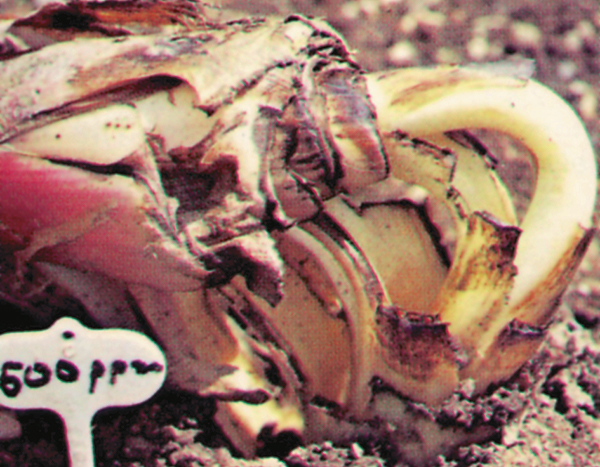
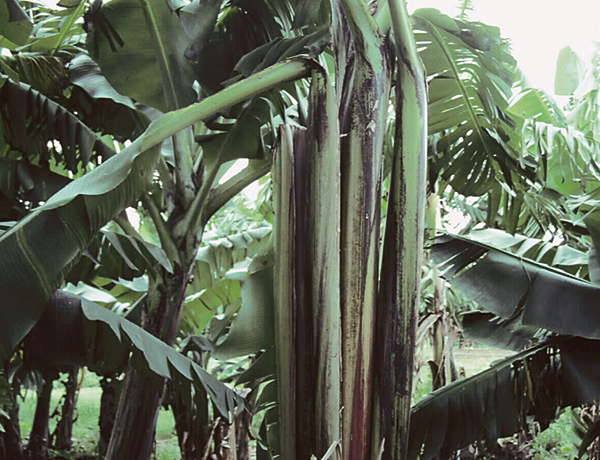
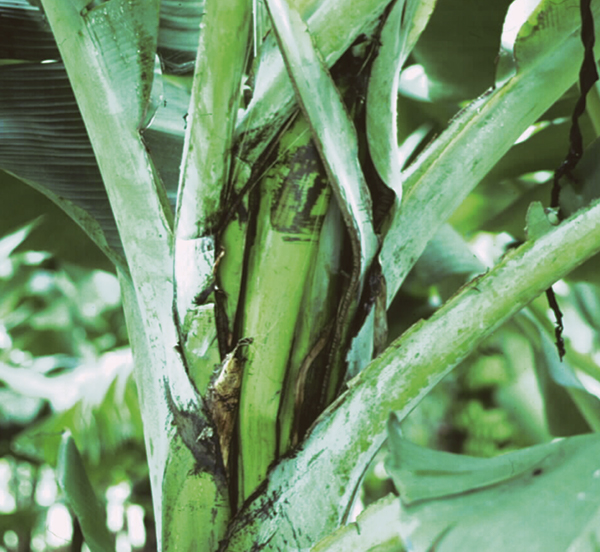
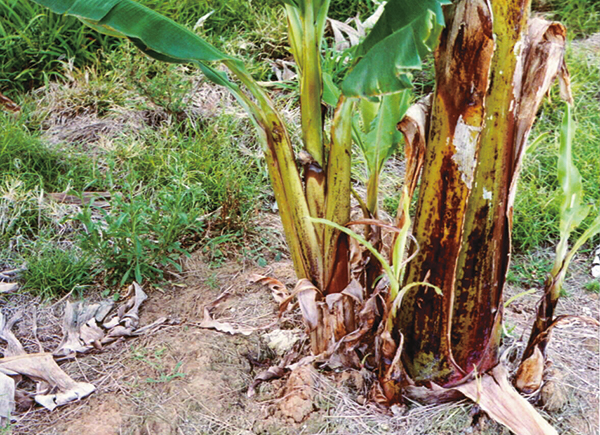
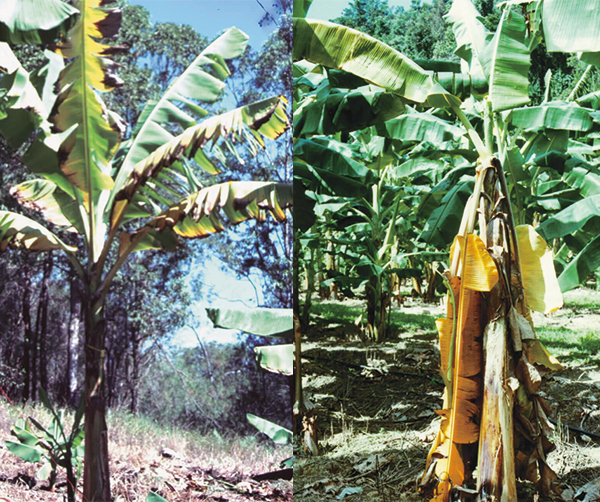
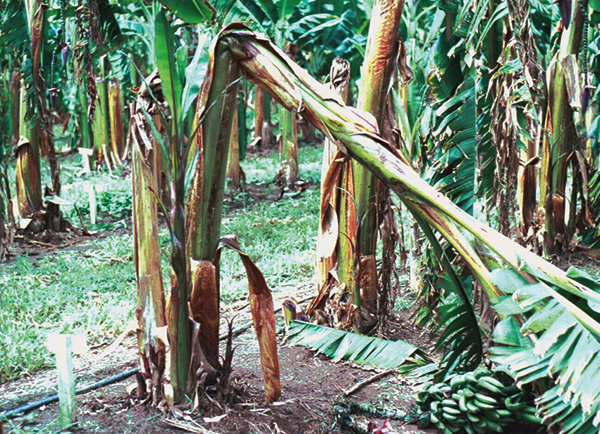
- Panama disease
- Postharvest
- Crop management
- Best management practices
- Pests, diseases & disorders
- On-farm biosecurity
- Subtropical banana research and resources
- Banana variety research
- Problem solver
- Videos
- Events
- Meet a Researcher
- Home
- About
- Research
- Banana variety research
- Agronomic evaluation of new varieties South Johnstone screening trials (December 2022)
- Agronomic evaluation of new varieties – South Johnstone screening trial (October 2020)
- Agronomic evaluation of new varieties – South Johnstone (2018)
- Developing new resistant varieties Goldfinger mutagenesis trial
- Panama TR4 variety screening trial – Northern Territory (2018)
- Panama R1 variety screening trial (New South Wales)
- Panama disease
- Postharvest
- Crop management
- Best management practices
- Pests, diseases & disorders
- On-farm biosecurity
- Subtropical banana research and resources
- Banana variety research
- Problem solver
- Videos
- Events
- Meet a Researcher
- Home
- About
- Research
- Banana variety research
- Agronomic evaluation of new varieties South Johnstone screening trials (December 2022)
- Agronomic evaluation of new varieties – South Johnstone screening trial (October 2020)
- Agronomic evaluation of new varieties – South Johnstone (2018)
- Developing new resistant varieties Goldfinger mutagenesis trial
- Panama TR4 variety screening trial – Northern Territory (2018)
- Panama R1 variety screening trial (New South Wales)
- Panama disease
- Postharvest
- Crop management
- Best management practices
- Pests, diseases & disorders
- On-farm biosecurity
- Subtropical banana research and resources
- Banana variety research
- Problem solver
- Videos
- Events
- Meet a Researcher
- Home
- About
- Research
- Banana variety research
- Agronomic evaluation of new varieties South Johnstone screening trials (December 2022)
- Agronomic evaluation of new varieties – South Johnstone screening trial (October 2020)
- Agronomic evaluation of new varieties – South Johnstone (2018)
- Developing new resistant varieties Goldfinger mutagenesis trial
- Panama TR4 variety screening trial – Northern Territory (2018)
- Panama R1 variety screening trial (New South Wales)
- Panama disease
- Postharvest
- Crop management
- Best management practices
- Pests, diseases & disorders
- On-farm biosecurity
- Subtropical banana research and resources
- Banana variety research
- Problem solver
- Videos
- Events
- Meet a Researcher